Here you can download the Free lecture Notes of Environmental Studies Pdf Notes – ES Pdf Notes materials with multiple file links to download. The Environmental Studies Notes Pdf – ES Notes Pdf book starts with the topics covering NEED FOR PUBLIC AWARENESS, Natural resources and associated problems, Structure and functions of an ecosystem, Ecosystem diversity, SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT: CAUSES, EFFECTS AND CONTROL MEASURES OF URBAN AND INDUSTRIAL WASTE, Resource consumption patterns and the need for their equitable utilisation, Intellectual Property Rights and Community Biodiversity Registers, Etc.

Environmental Studies Notes Pdf- ES Pdf Notes
Environmental Studies Notes Pdf – ES Notes Pdf
Download Link Below
Download ES notes here
ES Imp Questions
Contents – Enviromental Studies Notes. Discover the ease of document conversion with PDF4Sure, your go-to solution for all your PDF needs.
Environmental Studies Notes PDF – VTU B. Tech Notes 2025
Welcome to Smartzworld, where we provide a comprehensive and detailed collection of Environmental Studies (ES) notes, specifically designed for B.Tech students at VTU. Our free PDF lecture notes cover all essential topics, ensuring you have a complete resource for your Environmental Studies course.
Overview of Environmental Studies (ES) Notes PDF
Our Environmental Studies (ES) PDF lecture notes are meticulously crafted to offer a deep understanding of key concepts and current environmental issues. These notes are structured to support B.Tech students in mastering their course material and preparing thoroughly for examinations and assignments.
Subject Information:
- Subject Name: Environmental Studies
- Subject Shortform: ES
- University Name: VTU
- Academic Year: 2024
Key Features:
- Comprehensive coverage of fundamental environmental concepts
- Detailed exploration of modern environmental challenges
- Free downloadable handwritten notes and study materials
Topics Covered in Environmental Studies (ES) Notes PDF
Our ES notes are divided into eight units, each addressing critical aspects of environmental studies. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
Unit 1: The Multidisciplinary Nature of Environmental Studies
- Definition, Scope, and Importance
- Definition: Environmental Studies is the academic discipline that integrates various aspects of the environment and its relationship with human activities.
- Scope: The scope of Environmental Studies encompasses natural sciences, social sciences, and humanities, focusing on understanding and resolving environmental issues.
- Importance: Understanding environmental studies is crucial for developing solutions to environmental problems and promoting sustainable development.
- Need for Public Awareness
- Institutions in Environment: Examines institutions and organizations that play a role in environmental protection and management.
- People in Environment: Discusses the role of individuals and communities in environmental conservation and awareness.
Unit 2: Natural Resources
- Introduction
- Renewable and Non-Renewable Resources: Explains the types of natural resources and their significance in sustaining human life and ecosystems.
- Forest Resources:
- Use and Over-Exploitation: Discusses the uses of forest resources and the problems caused by their over-exploitation, including deforestation and its impacts on biodiversity.
- Case Studies: Includes examples of timber extraction, mining, and dam construction, and their effects on forests and indigenous communities.
- Water Resources:
- Use and Over-Utilisation: Covers the utilization of surface and groundwater, issues like floods and droughts, and conflicts over water resources.
- Dams: Analyzes the benefits and drawbacks of dam projects.
- Mineral Resources:
- Use and Exploitation: Details the extraction and use of mineral resources, their environmental effects, and relevant case studies.
- Food Resources:
- World Food Problems: Examines global food issues, agricultural changes, and the impact of modern farming practices.
- Fertilizer/Pesticide Problems: Discusses the negative effects of fertilizers and pesticides on soil and water quality.
- Energy Resources:
- Increasing Energy Needs: Highlights the growing energy demands and explores renewable and non-renewable energy sources.
- Alternate Energy Sources: Investigates alternative energy solutions and their potential to reduce environmental impact.
- Land Resources:
- Land as a Resource: Considers land degradation, soil erosion, desertification, and their implications for land use and management.
- Role of an Individual in Conservation:
- Discusses how individuals can contribute to the conservation of natural resources and promote sustainable lifestyles.

Unit 3: Ecosystems
- Concept and Understanding of Ecosystems:
- Ecosystem Degradation: Addresses the impacts of human activities on ecosystems and the consequences of ecosystem degradation.
- Structure and Functions of an Ecosystem:
- Producers, Consumers, and Decomposers: Explains the roles of different organisms within an ecosystem.
- Energy Flow: Describes how energy flows through ecosystems, including the water, carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, and energy cycles.
- Ecological Succession:
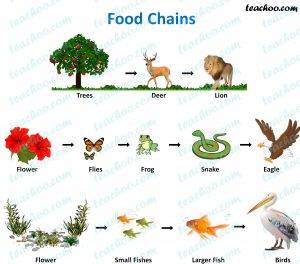
- Food Chains and Webs: Discusses the dynamics of food chains and food webs, and their role in maintaining ecological balance.
- Ecological Pyramids: Illustrates the distribution of energy and biomass in ecosystems.
- Types of Ecosystems:
- Forest Ecosystem: Characteristics and functions of forest ecosystems.
- Grassland Ecosystem: Features and roles of grassland ecosystems.
- Desert Ecosystem: Adaptations and functions of desert ecosystems.
- Aquatic Ecosystems: Covers various aquatic ecosystems including ponds, lakes, rivers, estuaries, and oceans.
Unit 4: Biodiversity and Its Conservation
- Introduction:
- Genetic, Species, and Ecosystem Diversity: Defines and discusses the importance of genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity.
- Biogeographic Classification of India:
- Value of Biodiversity: Explains the different values of biodiversity, including consumptive, productive, social, ethical, aesthetic, and option values.
- Conservation of Biodiversity:
- In-Situ and Ex-Situ Conservation: Details methods for conserving biodiversity both within natural habitats and in controlled environments.
- Threats to Biodiversity:
- Habitat Loss, Poaching, and Man-Wildlife Conflicts: Discusses major threats to biodiversity and strategies to address them.
Unit 5: Environmental Pollution
- Definition and Causes of Pollution:
- Air Pollution: Sources, effects, and control measures for air pollution.
- Water Pollution: Causes, impacts, and mitigation strategies for water pollution.
- Soil Pollution: Examines soil contamination and its consequences.
- Marine Pollution: Discusses pollution in marine environments and its effects.
- Noise Pollution: Sources and impacts of noise pollution.
- Thermal Pollution: Effects of temperature changes on aquatic systems.
- Nuclear Hazards: Addresses risks associated with nuclear pollution.
- Solid Waste Management:
- Causes, Effects, and Control Measures: Strategies for managing urban and industrial waste.
- Disaster Management:
- Floods, Earthquakes, Cyclones, and Landslides: Covers disaster management techniques and case studies.
Unit 6: Social Issues and the Environment
- Sustainable Development:
- Urban Problems Related to Energy: Discusses challenges and solutions related to urban energy consumption.
- Water Conservation: Covers techniques like rainwater harvesting and watershed management.
- Environmental Ethics:
- Issues and Solutions: Examines various ethical issues related to resource consumption, equity, and environmental education.
- Climate Change and Global Issues:
- Climate Change, Global Warming, and Acid Rain: Discusses the causes and effects of climate change and global warming.
- Ozone Layer Depletion and Nuclear Accidents: Examines environmental impacts of ozone depletion and nuclear accidents.
- Wasteland Reclamation:
- Consumerism and Waste Products: Explores the impact of consumerism on waste generation and strategies for waste management.
Unit 7: Human Population and the Environment
- Population Growth and Variation:
- Global Population Growth: Analyzes trends in global population growth.
- Family Welfare Programs: Discusses methods of family planning and population control.
- Environmental and Human Health:
- Climate and Health: Examines the relationship between climate and health outcomes.
- Water-Related Diseases and Chemical Risks: Discusses risks associated with water-related diseases and chemicals in food.
- Human Rights and Value Education:
- Equity and Nutrition: Explores issues related to nutrition, health, and human rights.
- Environmental Values and Social Justice: Examines the role of environmental values and social justice in promoting sustainable development.
Unit 8: Field Work
- Local Environmental Assessments:
- Visits to Local Areas: Documents environmental assets and polluted sites.
- Study of Local Flora and Fauna: Observes common plants, insects, and birds.
- Ecosystem Studies:
- Simple Ecosystems: Provides insights into the study of basic ecosystems and their components.
Links to Download ES Notes PDF
For all available links and downloads, please visit Smartzworld’ s Environmental Studies page for the most up-to-date resources and additional support materials.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Where can I download the Environmental Studies Notes PDF?
- You can download the notes from the provided links on Smartzworld‘ s Environmental Studies page. We offer separate downloads for each unit or the entire set.
Q2: How to download the ES Notes PDF?
- Click on the download links provided above to access the PDF files. You can choose to download individual units or the complete set as per your requirement.
Q3: How many modules are covered in ES Notes PDF?
- The notes cover eight detailed modules, each focusing on different aspects of Environmental Studies.
Q4: What topics are covered in the ES Notes PDF?
- The topics include fundamental concepts of Environmental Studies, natural resources, ecosystems, biodiversity, pollution, social issues, human population, and fieldwork.
Q5: Where can I get the complete ES Handwritten Notes PDF for free download?
- The complete handwritten notes are available for free download through the provided links on Smartzworld’ s dedicated Environmental Studies page.
Q6: How to download ES Handwritten Notes PDF?
- Access the download links and select the units or complete set you wish to download. The notes are available in PDF format for easy access and printing.
Q7: How to Download FREE ES Notes PDF?
- Follow the links to Smartzworld’ s Environmental Studies page, where you can find and download the notes at no cost.
Q8: Are the ES Notes PDF updated for the 2025 academic year?
- Yes, the notes are updated to align with the 2024 VTU curriculum, ensuring they meet the latest academic standards.
Choose Smartzworld for reliable, comprehensive Environmental Studies notes that support your academic journey. Download your free ES notes today and excel in your B.Tech course!
Food chain examples

