WRE-1 Notes Pdf – Water Resources Engineering-I Notes Pdf JNTU 2024

Water Resources Engineering-I Pdf Lecture Notes – JNTU
Welcome to the comprehensive resource for Water Resources Engineering-I (WRE-I) notes, specifically designed for B.Tech students at JNTU. These notes are created in accordance with the R09 syllabus, but they are also applicable for the R13 and R15 syllabi where the 8 units of the R09 syllabus have been consolidated into 5 units. Below, you will find detailed notes and download links for each unit.
Water Resources Engineering-I Notes Pdf
Below are the links to download the Water Resources Engineering-I notes:
Complete Notes
Unit 1 Notes
Unit 2 Notes
Unit 3 Notes
Unit 5 Notes
Overview of Water Resources Engineering-I Notes Pdf
The following sections provide an in-depth look at the topics covered in the Water Resources Engineering-I handwritten notes:
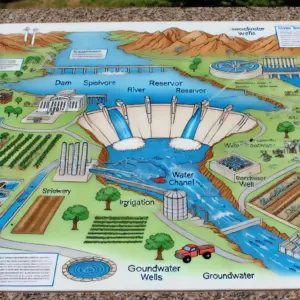
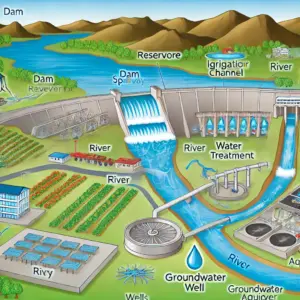
Unit-1: Hydrology and Hydrological Processes
- Overland Flow and Interflow: Understanding the movement of water over the land surface and the shallow subsurface flow that occurs when soil is saturated.
- Stream Flow and Groundwater Flow: Examining the dynamics of water flow in streams and rivers, and the movement of groundwater through aquifers.
- The Hydrograph and Photograph: Analyzing graphical representations of stream flow over time and the visual documentation of water bodies.
- Effective Rainfall: Calculating the portion of rainfall that contributes to runoff after accounting for losses like evaporation and infiltration.
- Methods of Base Flow Separation: Techniques to distinguish between base flow and direct runoff in a hydrograph. The third method uses a composite base flow recession curve, as illustrated in Figure 9.
Unit-2: Hydrographs and Catchment Characteristics
- Hydrograph and Catchment Characteristics: Understanding how the physical characteristics of a catchment area influence the shape and size of a hydrograph.
- Shape and Size of the Catchment: Assessing the impact of catchment shape and size on runoff and hydrograph formation.
- Effect of Spatial Distribution of Rainfall on Hydrograph: Exploring how the spatial variability of rainfall affects the runoff and hydrograph.
- Direction of Storm Movement: Analyzing how the path of storm movement influences the runoff pattern in a catchment.
- Rainfall Intensity: Studying the effect of varying rainfall intensities on the hydrograph.
- Application of the Unit Hydrograph: Utilizing unit hydrographs for predicting streamflow response to rainfall events in a given catchment.
Unit-3: Groundwater and Aquifers
- Water Table Contours and Regional Flow: Mapping the contours of the water table and understanding regional groundwater flow patterns.
- Aquifers and Confining Layers: Identifying different types of aquifers and the layers that confine groundwater flow.
- Continuity Equation and Darcy’s Law under Steady-State Conditions: Applying fundamental principles to describe the movement of groundwater under steady-state conditions.
- Steady One-Dimensional Flow in Aquifers: Analyzing groundwater flow in aquifers assuming steady, one-dimensional conditions.
- Aquifer with Constant Thickness: Examining flow through aquifers of uniform thickness.
- Wells and Tube Wells Installation: Techniques for the installation and development of wells and tube wells, including:
- Rotary Drilling Method: A method used to drill wells with rotary drills.
- Gravel Packing: Installing gravel around the well screen to prevent sand from entering the well.
- Flow Through Heterogeneous Media: Understanding the movement of water through aquifers with varying properties.
Unit-5: Design of Canals
- Lined or Non-Erodible, Unlined, Earthen, or Erodible Canals: Differentiating between various types of canal linings and their suitability for different conditions.
- Shape of the Cross-Section of the Canal: Designing the cross-sectional shape of canals to optimize flow and stability.
- Side Slope of the Canal: Determining the appropriate side slope to ensure the stability of canal banks.
- Longitudinal Bed Slope: Calculating the slope along the length of the canal to maintain desired flow conditions.
- Permissible Velocities – Maximum and Minimum: Ensuring that flow velocities remain within safe limits to prevent erosion or sedimentation.
- Roughness Coefficient: Using the roughness coefficient to account for the frictional resistance of the canal bed and sides.
- Freeboard: Providing adequate freeboard to prevent overtopping and ensure safety.
Links to Download Water Resources Engineering-I Notes Pdf
- WRE-I Notes and Study Material PDF Free Download
- Topics Covered in WRE-I Notes Pdf
- WRE-I Notes Pdf from JNTU
- Always Choose Smartzworld to download WRE-I Notes PDF
- Benefits of FREE WRE-I Handwritten Notes PDF
Why Choose Smartzworld for Your WRE-1 notes pdf ?
Smartzworld is dedicated to providing high-quality educational resources for students. By choosing Smartzworld, you gain access to meticulously prepared notes that cover all essential topics in Water Resources Engineering-I. The notes are tailored to help you understand complex concepts easily and perform well in your exams.
Benefits of FREE Water Resources Engineering-I Handwritten Notes PDF
- Comprehensive Coverage: All essential topics covered in detail.
- Easy to Understand: Simplified explanations for complex concepts.
- Accessible Anytime: Download and study at your convenience.
- Free of Cost: No charges for accessing high-quality educational material.
- Handwritten Notes: Authentic and reliable, offering a personal touch to your study material.
Download now
Topics Covered in Water Resources Engineering-I Notes
Hydrological Processes and Stream Flow Analysis
In the initial units, the focus is on the movement of water through various pathways in the hydrological cycle, including overland flow, interflow, streamflow, and groundwater flow. Understanding these processes is critical for predicting the response of catchments to rainfall and for managing water resources effectively. Effective rainfall calculation and methods for base flow separation are essential skills for water resources engineers, enabling them to distinguish between different components of streamflow and to design appropriate water management strategies.
Hydrograph Analysis and Catchment Characteristics
Hydrograph analysis is a fundamental aspect of hydrology, providing insights into how catchments respond to rainfall events. By studying the shape and size of catchments, the direction of storm movement, and the intensity of rainfall, engineers can predict streamflow patterns and design interventions to manage floods and droughts. The application of unit hydrographs simplifies the process of predicting streamflow from rainfall data, making it a valuable tool for water resources management.
Groundwater Flow and Aquifer Management
Groundwater is a critical component of the hydrological cycle, providing water for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use. Understanding the principles governing groundwater flow, such as Darcy’s law and the continuity equation, is essential for managing aquifers sustainably. Topics such as water table contours, regional flow patterns, and the design and installation of wells are covered in detail, equipping students with the knowledge needed to manage groundwater resources effectively.
Design and Management of Canals
The design of canals involves considerations of hydraulic efficiency, stability, and safety. By studying the different types of canal linings, cross-sectional shapes, side slopes, and bed slopes, students learn to design canals that can transport water efficiently while minimizing the risk of erosion and sedimentation. The calculation of permissible velocities and the selection of appropriate roughness coefficients are crucial for ensuring that canals function effectively under varying flow conditions.
FAQs about Water Resources Engineering-I Notes Pdf
Q1. Where can I download the Water Resources Engineering-I Notes Pdf?
- You can download the notes from the provided links for each unit or the complete set from Smartzworld.
Q2. How to download the Water Resources Engineering–I Notes Pdf?
- Click on the respective unit links or the complete notes link to download the PDF files.
Q3. How many modules are covered in WRE-1 Notes Pdf?
- The notes cover 5 units as per the R13 and R15 syllabus.
Q4. Topics Covered in Water Resources Engineering-I Notes Pdf?
- Topics include overland flow, stream flow, groundwater flow, hydrographs, effective rainfall, aquifers, Darcy’s law, and canal design among others.
Q5. Where can I get the complete WRE-I Handwritten Notes pdf FREE Download?
- The complete handwritten notes can be downloaded from the Smartzworld website.
Q6. How to download WRE-I Handwritten Notes pdf?
- Visit the Smartzworld website and click on the download links for the handwritten notes.
Q7. How to Download FREE Water Resources Engineering-I Notes PDF?
- Simply follow the links provided in this document to access the free download of the Water Resources Engineering-I Notes Free Download Click here
Download your Water Resources Engineering-I Notes today and take a step towards academic excellence in your B.Tech journey at JNTU!


