FE Notes pdf – The Foundation Engineering JNTU Download Free Lecture Notes
Here you can download the free lecture Notes of Foundation Engineering Pdf Notes – FE Pdf Notes materials with multiple file links to download. The Foundation Engineering Notes Pdf – FE Notes Pdf book starts with the topics covering Planning For Subsurface Exploration, DIFFERENT METHODS OF ANALYSIS, Semi Gravity Retaining Wall, Different types of footings, DESIGN METHODOLOGY FOR PILES, Etc.
Foundation Engineering Notes pdf – FE pdf notes – FE notes pdf file to download are listed below please check it –
Complete Notes
Unit 1
Unit 2
Unit 3
Unit 4
Unit 5
Note :- These notes are according to the R09 Syllabus book of JNTU.In R13 and R15,8-units of R09 syllabus are combined into 5-units in R13 and R15 syllabus. If you have any doubts please refer to the JNTU Syllabus Book.
Foundation Engineering Notes Pdf | FE Notes Pdf – JNTU B.Tech 2024
Welcome to the ultimate resource for Foundation Engineering Notes Pdf, designed specifically for B.Tech students at JNTU for the academic year 2024. This document compiles comprehensive lecture notes covering all critical aspects of foundation engineering. Whether you are preparing for exams or need a reference for projects, these notes provide detailed insights into subsurface exploration, analysis methods, retaining walls, footings, and pile design.
Overview of Foundation Engineering
Foundation engineering is a branch of civil engineering that deals with the design and analysis of structures that support buildings and other constructions. The foundation is a critical component that transfers loads from the structure to the ground. A well-designed foundation ensures the stability and longevity of the structure, making foundation engineering a vital field of study.
This set of notes covers the fundamental concepts and advanced techniques used in foundation engineering. It aligns with the R09 syllabus of JNTU and has been updated to reflect changes in the R13 and R15 syllabi, combining 8-units into 5-units for streamlined learning.
Foundation Engineering Lecture Notes – University Name
This section introduces the subject and its relevance to the field of civil engineering. Foundation engineering involves understanding soil mechanics, structural load-bearing capabilities, and the principles behind the design of various foundation types. The notes encompass theoretical foundations and practical applications, making them a valuable resource for students and professionals alike.
Topics Covered in Foundation Engineering Handwritten Notes
Unit 1: Planning for Subsurface Exploration
Subsurface exploration is the first step in foundation design. It involves understanding the soil and rock beneath a construction site to determine its suitability for supporting a structure. Here are the key topics covered in this unit:
- Types of Boring
Boring is a technique used to investigate subsurface conditions. Various methods include:- Displacement Borings: This involves advancing a boring tool into the ground to displace soil. It is commonly used in cohesive soils.
- Wash Boring: This method uses a rotating drill bit and water or drilling fluid to remove soil and bring samples to the surface.
- Planning and Fact Finding
Effective subsurface exploration requires thorough planning and data collection:- Geological Survey: Conducting geological surveys to identify the physical characteristics of the site.
- Reconnaissance: Initial site visits and observations to gather preliminary data.
- Auger Boring
A method using a helical screw blade called an auger to drill into the soil and bring up samples:- Undisturbed Samples: Obtaining samples that accurately reflect the in-situ conditions of the soil is crucial for analysis.
- Requirement of Good Sampling Process: Ensures that samples are representative and free from contamination.
- Penetrometer Tests
These tests determine the resistance of soil to penetration, helping to assess its strength:- Standard Penetration Test (SPT): A widely used test that provides an indication of soil density and strength by measuring the resistance to penetration of a standard sampler.
Understanding subsurface conditions is essential for selecting the appropriate foundation type and design. The data collected during exploration informs the decision-making process and helps mitigate potential risks.
Unit 2: Methods of Analysis
This unit covers various analytical methods used in foundation engineering to assess soil behavior and design structures accordingly. Different methods are employed depending on the complexity and requirements of the project:
- Introduction to Analytical Methods
Understanding the principles behind different analytical techniques is crucial for accurate foundation design. - Rankine Earth Pressure
This classical theory calculates lateral earth pressures exerted by soil:- Earth Pressure Coefficients: Determine the magnitude of pressure based on soil type and conditions.
- Inclined Ground: Analyzing scenarios where the ground surface is inclined, affecting pressure distribution.
- Limit Equilibrium
A method that assumes soil mass is on the verge of failure, helping predict stability:- Limit Analysis: Evaluates the potential for collapse or failure within a soil mass.
- Method of Characteristics: Uses mathematical characteristics to solve problems related to stress distribution in soils.
- Finite Element / Discrete Element Method
Advanced numerical methods used for complex soil-structure interactions:- Finite Element Method (FEM): Breaks down a complex problem into smaller, manageable elements for analysis.
- Discrete Element Method (DEM): Simulates the behavior of individual particles within a material to predict movement and interaction.
- Theorems in Soil Mechanics
Fundamental theorems that provide the basis for many analytical methods, such as:- Mohr-Coulomb Failure Criterion: Describes the shear strength of soils based on cohesion and internal friction.
These methods form the backbone of foundation engineering, enabling engineers to design safe and effective foundations for a variety of structures.
Unit 3: Retaining Walls
Retaining walls are structures designed to hold back soil or rock from a building or other structure. They are essential in situations where there is a significant change in ground elevation:
- Types of Retaining Walls
Various types of retaining walls are used depending on site conditions and requirements:- Gravity Walls: Use their own weight to resist earth pressures.
- Semi-Gravity Retaining Walls: Combine mass and reinforcing elements for stability.
- Counterfort Retaining Walls: Utilize triangular-shaped supports (counterforts) on the back of the wall to reduce bending moments.
- Flexible Walls: Adapt to soil movement, suitable for areas with high seismic activity.
- Sheet Pile Walls
Thin walls driven into the ground to retain soil or water:- Cantilever Sheet Pile Walls: A single row of sheet piles anchored by the soil on either side.
- Free Cantilever Sheet Pile: Extends above ground without additional support.
- Anchored Sheet Pile Walls: Use anchors to provide additional support and stability.
- Free Earth Support Piles and Fixed Earth Support Piles
Piles used to support structures where soil conditions vary:- Free Earth Support: Piles that provide lateral support without rigid connections.
- Fixed Earth Support: Piles with rigid connections to the structure, providing greater stability.
Retaining walls must be carefully designed to withstand lateral earth pressures and potential ground movement, ensuring the safety and integrity of the supported structure.
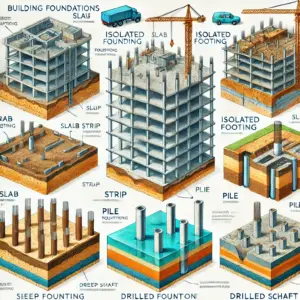
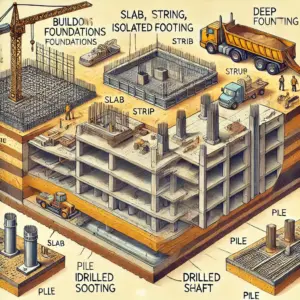
Unit 4: Different Types of Footings
Footings are structural elements that transfer loads from buildings or structures to the ground. They are a crucial part of the foundation system, providing stability and support:
- Introduction to Footings
Footings come in various shapes and sizes, each designed for specific conditions and load requirements. - Types of Footings
Different types of footings are used depending on soil conditions and structural demands:- Isolated Footings: Used to support individual columns, transferring loads directly to the soil.
- Combined Footings: Support multiple columns, distributing loads over a larger area.
- Strip Footings: Continuous footings that support walls or rows of columns.
- Raft or Mat Footings: Large continuous slabs that support the entire structure, suitable for weak or compressible soils.
- Design Considerations
Key factors in the design of footings include:- Flexural Reinforcement: Ensures that footings can withstand bending stresses.
- Development Length: The minimum length of reinforcement needed to transfer stress between steel and concrete.
- Load Transfer at Base of Column: Effective transfer of structural loads to the footing.
- Determination of Size and Design Soil Pressure
Calculating the appropriate size and pressure for footings involves:- Size of Column and Footing: Determined based on load requirements and soil conditions.
- Design Soil Pressure: The maximum pressure the soil can safely support without risk of settlement or failure.
Footing design is critical to ensuring that the structure can safely and efficiently transfer loads to the ground, maintaining stability and preventing structural issues.
Unit 5: Design Methodology for Piles
Piles are deep foundation elements used to transfer loads to deeper, more stable soil layers or rock. This unit covers the essential principles and practices involved in pile design:
- Introduction to Piles
Piles are used in situations where shallow foundations are not feasible due to weak or unstable surface soils. - Design Methodology
Key considerations in pile design include:- Requirement for Deep Foundations: Factors influencing the choice of deep foundations over shallow ones.
- Classification of Piles: Various types of piles used based on material, installation method, and load-bearing capacity.
- Points to Consider for Choosing Piles
Selecting the appropriate type of pile involves several considerations:- Soil Conditions: Understanding the soil profile and its bearing capacity.
- Load Requirements: Determining the load-bearing capacity needed for the structure.
- Environmental Factors: Considering factors such as water table level and seismic activity.
- Pile Installation Techniques
Different methods are used to install piles, each suited to specific site conditions:- Driven Piles: Installed by hammering into the ground, suitable for dense soils.
- Bored Piles: Drilled into the ground and filled with concrete, ideal for sites with soft soils or obstructions.
- Screw Piles: Installed by screwing into the ground, offering rapid installation and minimal disturbance.
Piles play a crucial role in providing deep foundations for structures, ensuring stability and load distribution in challenging soil conditions.
Download Foundation Engineering Notes Pdf
Below are the links to download the complete set of Foundation Engineering Notes, organized by unit. These notes provide comprehensive coverage of all topics and are an essential resource for students and professionals alike.
- Complete Notes
Link: Complete Notes - Unit 1 Notes
Link: Unit 1 Notes - Unit 2 Notes
Link: Unit 2 Notes - Unit 3 Notes
Link: Unit 3 Notes - Unit 4 Notes
Link: Unit 4 Notes - Unit 5 Notes
Link: Unit 5 Notes
Benefits of FREE Foundation Engineering Handwritten Notes PDF
Choosing the right resources for your studies is crucial, and these Foundation Engineering Handwritten Notes offer several benefits:
- Comprehensive Coverage: These notes cover all essential topics in foundation engineering, aligned with the JNTU syllabus.
- Accessibility: Easily downloadable PDFs allow you to study offline at your convenience.
- Structured Learning: The notes are organized according to university syllabus, making it easy to follow and understand.
- Expert Insights: Handwritten notes provide insights and explanations from experienced educators.
- Cost-Effective: Access to free, high-quality educational materials without the need for expensive textbooks.
By utilizing these notes, students can enhance their understanding of foundation engineering concepts and principles, leading to academic success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Where can I download the Foundation Engineering Notes Pdf?
You can download the notes from the provided links for each unit or the complete set from Smartzworld.
Q2. How to download the FE Notes Pdf?
Click on the respective links provided for each unit or the complete notes to initiate the download.
Q3. How many modules are covered in FE Notes Pdf?
Five units are covered, each addressing key topics in foundation engineering as per the JNTU syllabus.
Q4. Topics Covered in FE Notes Pdf?
The notes cover subsurface exploration, methods of analysis, retaining walls, footings, and pile design methodology.
Q5. Where can I get the complete FE Handwritten Notes pdf FREE Download?
The complete set of handwritten notes can be downloaded from the links provided in this document.
Q6. How to download FE Handwritten Notes pdf?
Access the links for each unit or the complete notes for a free download.
Q7. How to Download FREE FE Notes PDF?
Choose Smartzworld for a seamless download experience of FE notes PDFs.
Always choose Smartzworld for the latest and most comprehensive Foundation Engineering Notes Pdf for your academic success! By utilizing these resources, students can gain a deeper understanding of foundation engineering principles and apply them effectively in their academic and professional careers.


