What is Parkinson’s disease?
Parkinson’s disease (PD) also known as Parkinsonism is a degenerative illness that affects the brain parts which control your body movement. This illness often causes tremors. Parkinson’s disease is common in elderly people about 60 years or above. It is sometimes also possible to happen to younger people but the chances are rare.
The disease is a nervous system disorder and has an increasing effect on the patient’s body. The initial stage of the disease may have an unnoticeable tremor and that is in only one hand. Later on, it rapidly progresses towards severe handshaking and finally makes it utterly difficult for one to even hold a glass in hands.
Parkinson’s disease is characterized by several tremors and is also causes by slowing down the movement or stiffness. Parkinson’s is a progressive nervous system disorder that affects the body’s movement.
In Parkinson’s disease early stages, a person’s face might show little or no expressions. The patient’s hands might not swing while walking, speech may get soft or slurred. With time, the condition worsens and impacts of symptoms progress while the patient talk, sleep or think.
Parkinson’s Disease Causes
The exact cause of Parkinson’s is yet unknown by scientists. Both genetic and environmental aspects can cause Parkinson’s disease.
Parkinson’s is a diverse disease. No two people ever get affected by it in the same way. Around 1 million people in the USA and around 10 million people worldwide get affected with Parkinson’s every year.
The patient’s brain suffers from the loss of dopamine and norepinephrine in the substantia nigra area of the brain.
Genetics
Genetics is the reason for almost 10 o 15 per cent of total Parkinson’s. Scientists have discovered dozens of gene mutations is linked with the disease. These mutations are not common except with the rare cases of several family members suffering from Parkinson’s disease.
Environmental Triggers
Parkinson’s sometimes caused by exposure to certain toxins or some other environmental factors may increase the risk of PD.
Parkinson’s disease causes include both genetics, environmental trigger and lifestyle influences.
Read More:
Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of Parkinson’s disease may vary in every person. Early signs are often mild and go unnoticed. Symptoms of Parkinson’s generally start with one side of the body and stays worse on that side, even though both sides have started to show symptoms.
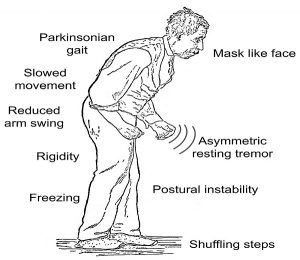
Parkinson’s symptoms and signs may include:
- Tremor: A tremor, or shaking, generally starts in a limb, hand or fingers. A person may rub his/her thumb and forefinger back and forth; this rubbing is known as a pill-rolling tremor. The patient’s hand may tremble even when it’s at rest.

Tremor in one hand is an early sign of Parkinson’s disease - Slowed movement (bradykinesia): With time, Parkinson’s disease may slow body movement, making simple tasks more difficult and time-consuming. Patient’s steps may become shorter when they walk. It may get difficult to get up from a chair. The patient may have to drag his/her feet as they try to walk.
- Rigid muscles: Muscle stiffness may also occur in any body part. The stiff muscles can be painful and limit the range of motion.
- Impaired posture and balance: Posture may become stooped, or the patient may have balance problems.
- Loss of automatic movements: A person may face a decreased ability to perform unconscious movements such as blinking, smiling or swinging arms while walking.
- Speech changes: A person may speak softly, quickly, slur or hesitate before talking. Speech may be more of a monotone than having the usual inflections.
- Writing changes: A person may face hardship while writing, and writing may appear small.
Prevention of Parkinson’s Disease
Pesticides often increase the risk of Parkinson’s. While using pesticides and other toxins, appropriate protection is the utmost necessary to reduces the risk of Parkinson’s.
Preventing Parkinson’s entirety is not possible but some studies have proved that some habits may help in preventing the risk of Parkinson’s.
- Use turmeric: Turmeric contains curcumin, which is an antioxidant ingredient. Consuming turmeric may help in preventing the clumping of a protein that plays a role in Parkinson’s, as per one laboratory study.
- Use flavonoids: Consuming some other antioxidants such as the flavonoids, may often help in reducing the risk of developing Parkinson’s. Flavonoids are present in berries, apples, some vegetables, tea, and also red grapes.
- Avoid reheated cooking oils: As per some studies that have linked the toxic chemicals, which are known as aldehydes, to the Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s and some other neurodegenerative diseases, and also some of the cancers.


