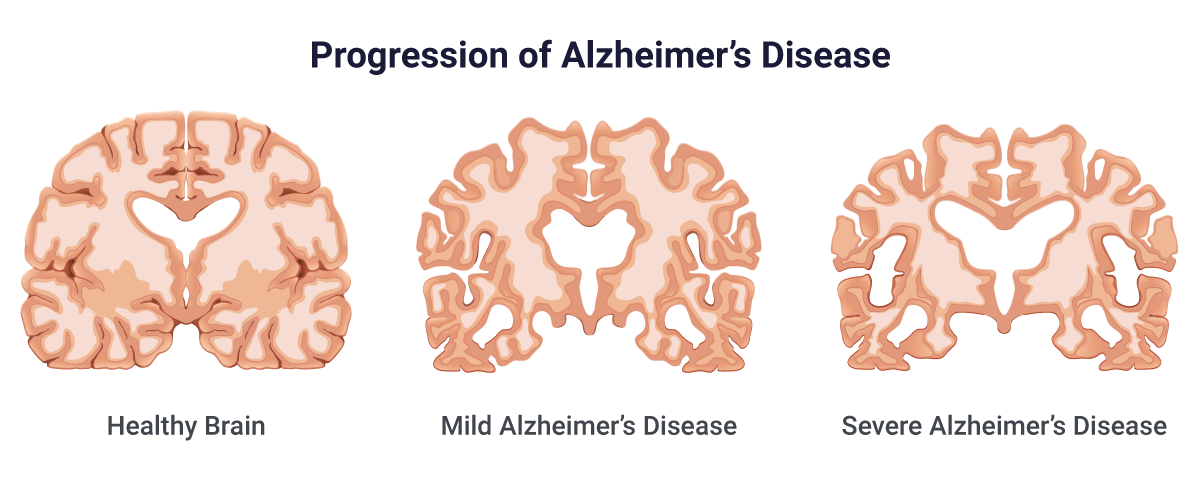
What is Alzheimer’s disease?
Alzheimer’s disease is a neurological disorder in which the brain cells degenerate, which leads to memory loss along with the cognitive decline.
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common type of dementia, which accounts for 60 to 80 per cent of cases of dementia in the U.S.
In the year 2013, about 6.8 million people in the U.S. have been diagnosed with dementia. Out of these, nearly 5 million had a diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. By the year 2050, the number is expected to double.
Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative disease. Symptoms are mild at the initial stages, but they become much more severe over time. This disease is a progressive disorder that usually causes brain cells to waste away or degenerate and then die. Alzheimer’s disease is the common cause of dementia which is a continuous decline in their thinking, behavioral and also social skills that disrupts the ability of a person to function independently.
Signs of this disease include forgetting recent events or conversations. As long as the disease progresses, a person suffering with Alzheimer’s disease will develop memory impairment and may also lose the ability to carry out their everyday tasks.
Read More – 10 Tips on How to Get Glowing Skin
What are the Causes of Alzheimer’s Disease?
Researchers till date do not fully understand the main cause of Alzheimer’s disease in most people. In some people with the early onset of Alzheimer’s disease, a genetic mutation might be the cause. Also, the late-onset of Alzheimer’s arises from the complex series of brain changes that may occur over the decades.
Causes of Alzheimer’s disease probably include a combination of genetic, environmental, and also lifestyle factors. The main importance of any of these factors might be in increasing or decreasing the risk of developing this disease as it may differ from person to person.
Few scientists are also conducting some studies to learn more about the plaques, tangles, and many other biological features of this condition. Few advances in the brain imaging techniques might allow the researchers to see that the development and spread of the abnormal amyloid and tau proteins which are in the living brain, as well as the changes which are in brain structure and function.
Few scientists are by now exploring the very early steps in the disease process by studying the changes in the brain and the body fluids that can be detected years before the Alzheimer’s symptoms appear.
Follow us on FB for more – Health Care & Fitness Tips – Smartzworld
What are the Symptoms of Alzheimer’s Disease?
A person suffering from Alzheimer’s disease will eventually need full-time assistance. In order to receive a diagnosis of the Alzheimer’s condition, the person must have experienced a decline in the cognitive or behavioral function. And their performance must be compared with how they were previously. The decline in their activities and behavior must interfere with their ability to function at work or in their usual activities.
Symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease:
Their cognitive decline must be seen in at least two of the five main symptom areas which are listed below:
1. Their reduced ability to grab and remember new information, which can generally lead to, for example:
- Asking repetitive questions or repeating the same conversations.
- Misplacing personal belongings.
- Forgetting events or any important appointments.
- Getting lost on a very familiar route.
2. They usually suffer from reasoning impairment, any complex tasking, and also exercising judgment, such as:
- Their poor understanding about safety risks.
- They will not be able to manage finances.
- Generally, they will have poor decision-making ability.
- They will not be able to plan any complex or sequential activities in their daily life.
3. They might have any impaired visuospatial abilities that are generally not seen, for example, some might be due to eye sight problems. They could be:
- They will not have the ability to recognize faces or any common objects or to find any objects that are in their direct view.
- Their inability to use any simple tools or equipment, for example, to orient their own clothing to the body.
4. They will have an impaired speaking, reading and writing, for example:
- They may have difficulty in thinking of common words while they are speaking or hesitations.
- They might have difficulty in speech, spelling, and writing errors.
5. Some changes may be noticed in their personality and behavior, such as:
- Their out-of-character mood swings like agitation, apathy, social withdrawal or sometimes lack of interest, motivation, or any initiative.
- Sometimes, language problems can also be an early key symptom like struggling to find the right words.
- Their inability to recognize objects and faces.
- Difficulty in comprehending separate parts of a scene at once.
- Difficulty with reading text, often known as alexia.
The most prominent deficit in this condition is in the executive dysfunction which would be to do with the reasoning, judgment, and problem-solving.
What is the Treatment of Alzheimer’s disease?
The current day Alzheimer’s disease medications might temporarily improve the symptoms or may also slow down the rate of decline. The treatments of this disease can sometimes help people suffering with Alzheimer’s disease to maximize function and also maintain independence for a time.
As of now, no treatment cures Alzheimer’s disease or may alter the disease process in the brain. In the advanced stages of this Alzheimer’s disease, complications from severe loss of brain function such as dehydration, malnutrition or infection might result in death.
Some FAQs
1. What is the main cause of Alzheimer’s?
The disease is thought to be caused by the abnormal build-up of proteins in and around brain cells. One of the involved proteins is called amyloid. Deposits of amyloid form plaques around brain cells. The other one is called tau, and its form tangles within brain cells.
2. What are the 7 stages of Alzheimer’s?
The following are the 7 stages of Alzheimer’s:
- Stage 1: No Impairment – During this stage, Alzheimer’s is not detectable and no memory problems or other symptoms of dementia are evident.
- Stage 2: Very Mild Decline – Seniors may notice minor memory problems. The person will still do fine on memory tests and the disease is most likely to be not detected by loved ones or physicians.
- Stage 3: Mild Decline – At this stage, family members may notice the memory loss problem of seniors. The tests of Alzheimer’s disease patients also become detectable.
- Stage 4: Moderate Decline – All the signs of Alzheimer’s disease become detectable at this stage.
- Stage 5: Moderately Severe Decline – Patients begin to need help with many day-to-day activities.
- Stage 6: Severe Decline – Alzheimer’s disease patients need constant supervision and frequently require professional care at the 6th stage of the disease.
- Stages 7: Very Severe Decline – It is the final stage of Alzheimer’s disease as it is a terminal illness and the patient in stage seven is nearing death.